Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Smart Contracts on Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions embedded in code, residing on a blockchain. These digital contracts enable two or more parties to interact directly without intermediaries while ensuring transparency, immutability, and automation. The code executes the terms of the contract automatically once the predefined conditions are met, leaving no room for manipulation or ambiguity.
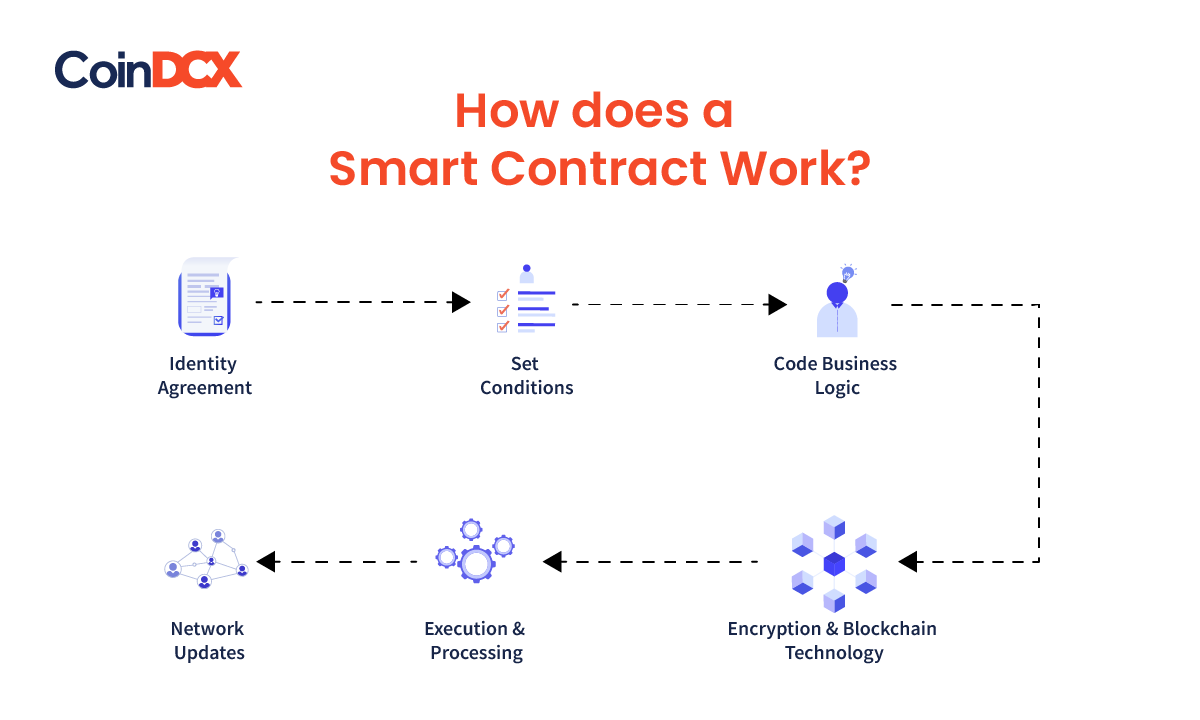
How do Smart Contracts Work?
- Blockchain Platform: Smart contracts are typically implemented on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, EOS, or Binance Smart Chain. These platforms provide the necessary infrastructure and support for executing smart contracts.
- Contract Deployment: A developer writes the smart contract code using a specific programming language supported by the blockchain platform. The code specifies the conditions, rules, and actions to be executed within the contract.
- Contract Deployment and Address: The developer deploys the smart contract onto the blockchain network by submitting it as a transaction. Once deployed, the contract is assigned a unique address that identifies it on the blockchain.
- Interacting with the Contract: Users can interact with the smart contract by sending transactions to its address. These transactions trigger the execution of the code within the contract, and the contract’s state may be updated accordingly.
- Validation and Consensus: When a transaction involving a smart contract is submitted, it is validated and processed by the blockchain network’s nodes through a consensus mechanism (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake). This ensures that the transaction is legitimate and conforms to the network’s rules.
- Code Execution: Once the transaction is validated and included in a block, the nodes execute the code within the smart contract. The contract’s predefined conditions, rules, and actions are carried out automatically without the need for intermediaries or manual intervention.
- State and Storage: Smart contracts maintain their state and data on the blockchain’s decentralized ledger. The contract’s state reflects the values of variables and data stored within it. The state is updated as transactions modify the contract’s data.
- Immutability and Security: Smart contracts are immutable once deployed on the blockchain. They cannot be altered or tampered with, ensuring the integrity and security of their execution and data. The decentralized nature of blockchain provides resilience against single points of failure and enhances trust.
- Event Triggering: Smart contracts can emit events during their execution. These events can be captured by external applications or other smart contracts, enabling interactions and the creation of complex decentralized applications (DApps) that utilize multiple smart contracts.
- Transaction Settlement: Smart contracts can handle the transfer of digital assets, such as cryptos, as part of their execution. These transfers occur automatically based on the predefined conditions within the contract, providing secure and trustless transactions.
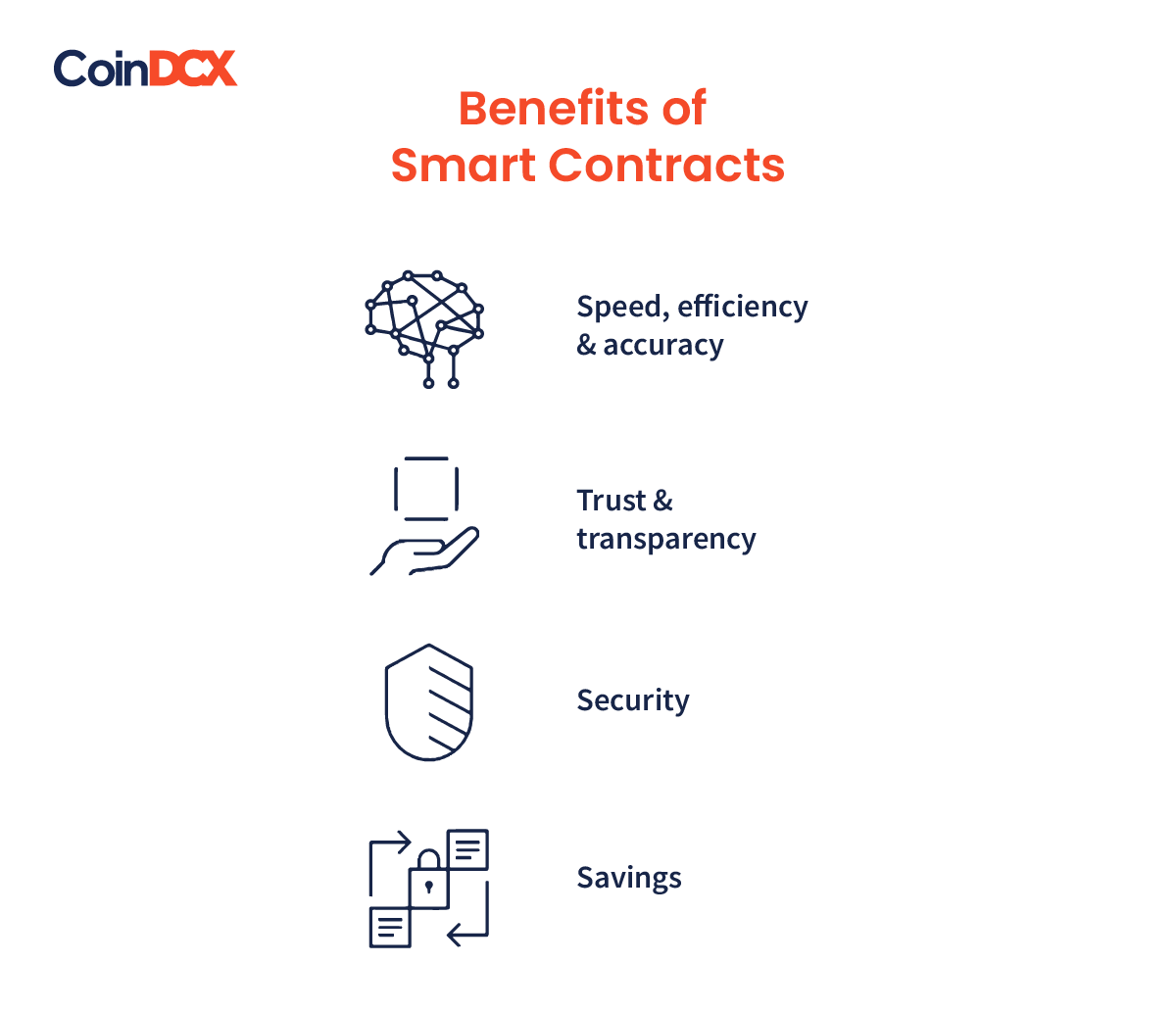
Benefits Of Smart Contracts
- Trust and Transparency: Smart contracts operate on a blockchain, which is a decentralized and immutable ledger. Every transaction and contract execution is recorded and visible to all participants. This transparency builds trust among parties involved, as they can independently verify and audit the actions and outcomes of the contract.
- Automation and Efficiency: Smart contracts automate the execution of predefined conditions and actions, reducing the need for manual intervention and paperwork. This automation streamlines processes, eliminates intermediaries, and minimizes human errors, resulting in increased efficiency and faster transaction times.
- Security and Reliability: Blockchain-based smart contracts leverage cryptographic techniques, ensuring high levels of security. Once deployed, smart contracts become tamper-resistant and immutable, making them highly reliable and resistant to fraud or unauthorized modifications. This enhances the overall security of agreements and reduces the risk of disputes.
- Cost Savings: By removing intermediaries and automating contract execution, smart contracts reduce costs associated with traditional processes. Parties can save on administrative expenses, third-party fees, and paperwork. Additionally, the automation of tasks minimizes the potential for errors, delays, and the need for dispute resolution, further reducing costs.
- Accuracy and Consistency: Smart contracts execute actions based on predefined conditions with precision and consistency. They eliminate the possibility of misinterpretation or miscommunication, as the terms and rules are explicitly coded into the contract. This ensures that all parties involved receive the same accurate information, reducing misunderstandings and disputes.
- Speed and Efficiency in Dispute Resolution: In case of disputes, smart contracts can streamline the resolution process. As all relevant information and actions are recorded on the blockchain, the parties involved can easily access the necessary data to resolve conflicts more efficiently and effectively. This reduces the time, effort, and costs associated with traditional dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Traceability and Auditability: Smart contracts provide a transparent and auditable record of all actions and transactions on the blockchain. This traceability ensures accountability and enables parties to track and verify the history of interactions related to the contract. It becomes easier to trace assets, verify ownership, and monitor compliance with contractual obligations.
- Flexibility and Customization: Smart contracts can be tailored to meet specific requirements and conditions of various agreements. They offer flexibility in defining rules, parameters, and actions, allowing parties to create contracts that suit their unique needs. This customization capability expands the potential applications of smart contracts across diverse industries.
Challenges Of Smart Contracts
- Security Risks: Smart contracts are vulnerable to security risks, including coding errors, software bugs, and flaws in the underlying blockchain platform. If not thoroughly audited and tested, these vulnerabilities can be exploited, leading to financial losses or unauthorized access.
- Immutability: Once a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be easily modified or reversed. This poses a challenge if there are errors or unforeseen circumstances that require contract updates or amendments.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Smart contracts can potentially replace traditional legal agreements, but the legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding them are still evolving. Determining the legal validity and enforceability of smart contracts in different jurisdictions can be complex.
- Lack of Standardization: Smart contracts are implemented on various blockchain platforms, each with its own programming language and features. The lack of standardization makes it difficult to port or interoperate smart contracts across different blockchain networks.
- Oracles and External Data: Smart contracts often require external data to execute their predefined conditions accurately. However, retrieving reliable and tamper-proof data from external sources (through oracles) can be challenging and introduces potential points of failure or manipulation.
- Scalability and Performance: Blockchain networks, including those hosting smart contracts, often face scalability and performance limitations. As the number of users and transactions grows, bottlenecks may occur, leading to increased costs and slower execution times.
- User Experience and Accessibility: Interacting with smart contracts typically requires users to have some technical knowledge and familiarity with blockchain technology. Improving user experience and making smart contract interactions more accessible to a broader audience remain ongoing challenges.
Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have a wide range of use cases across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can automate and streamline supply chain processes, such as tracking and verifying the movement of goods, managing inventory, and facilitating payments between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
- Financial Services: Smart contracts enable secure and transparent financial transactions, including peer-to-peer lending, decentralized crowdfunding, insurance claims processing, automatic payments, and cross-border remittances, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing costs.
- Real Estate: Smart contracts can simplify and automate property transactions, such as buying, selling, and renting real estate. They help ensure transparency, reduce paperwork, and enable the efficient transfer of property ownership by automatically executing agreed-upon conditions.
- Intellectual Property: Smart contracts can facilitate the protection and management of intellectual property rights by enforcing licensing agreements, tracking usage, and automatically distributing royalties to content creators, musicians, artists, and authors.
- Healthcare: Smart contracts can improve the security and privacy of patient data, automate insurance claims processing, enable efficient sharing of medical records between healthcare providers, and facilitate the execution of research contracts and clinical trials.
- Voting Systems: Smart contracts can be used to create transparent and tamper-proof voting systems. By recording votes on a blockchain, smart contracts can ensure the accuracy, integrity, and suitability of the voting process, reducing fraud and enhancing trust.
- Energy Trading: Smart contracts can enable peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess renewable energy directly, reducing reliance on centralized energy providers, and promoting sustainability.
- Gaming and Digital Assets: Smart contracts can be used in online gaming to ensure fairness, automate in-game purchases and rewards, and enable secure and transparent trading of digital assets, such as virtual goods, collectibles, and crypto assets.
Conclusion
In a world where trust meets technology, smart contracts emerge as the witty superheroes of agreements. They boast transparency, automation, and security, making traditional contracts blush with envy. With their impeccable accuracy, they make streamlined efficiency possible for everyone. Smart contracts are the sassy revolutionaries reshaping industries, saving costs, and bringing a smile to the face of anyone who loves a little wit in their transactions. So, grab your popcorn and watch as smart contracts steal the show, leaving old-school contracts in their dust. Or, as some crypto enthusiasts believe, it is a smart move in a digital world.
FAQs
With so many new projects coming up every day in the Web3 world, it becomes tough to keep a tab on the various names. Here are the top 5 smart contracts blockchains: Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, Corda, Stellar, and Rootstock. Given the vast stature in which smart contracts are being explored on the Web3 space, the example of a smart contract in a blockchain will be its usage for financial services, among others. The infamous altcoin, Ethereum is the most used blockchain for smart contracts.What are the top 5 smart contract blockchains?
What is an example of a smart contract in blockchain?
What is the most used blockchain for smart contracts?
Related posts
How Blockchain Is Revolutionising the NFT Gaming Scene
Blockchain and NFTs are transforming the gaming industry’s future.
Read more
What is the Difference Between Crypto Assets and Blockchain?
Blockchain is revolutionizing industries far beyond crypto applications.
Read more


